Introduction Global infrastructure projects are the foundation of economic growth, connectivity, and improved access to essential services. They also encourage international cooperation. These projects are essential for meeting the demands of a world that is changing at a rapid rate. They range from massive transportation networks and facilities for renewable energy to digital infrastructure and urban development. This daily update provides an overview of the most recent developments in global infrastructure, focusing on key projects, emerging trends, and the broader repercussions for progress in social and economic development.
Developments and Major Infrastructure Projects
1. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
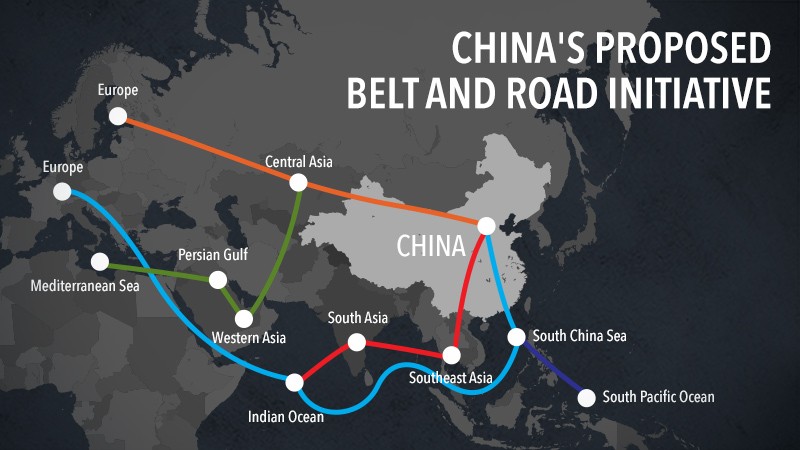
China continues to be one of the largest and most ambitious infrastructure projects on a global scale, with a significant focus on Africa. China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) expands into Africa.
Recent Happenings:
Kenya, Nigeria, and Ethiopia are just a few of the African nations that have signed new agreements with China to build important infrastructure like highways, ports, and railways.
The Lamu Port-South Sudan-Ethiopia Transport (LAPSSET) Corridor project in Kenya, which is part of the BRI, has made a lot of progress with the completion of important segments like a new port and a highway.
In support of sustainable development, China has also pledged additional investments in renewable energy infrastructure across the continent, focusing on solar and wind projects.
Financial Impact:
It is anticipated that these projects will expand trade routes within Africa and with global markets, reduce transportation costs, and improve regional connectivity.
The BRI has received praise for its potential to boost economic growth, but it has also been criticized for its debt sustainability and some projects’ impact on the environment.
2. The European Union

Making significant investments in green infrastructure as part of its Green Deal to achieve its ambitious climate goals and transition to a sustainable economy.
Important Tasks:
Offshore wind farms are getting huge investments from the EU, with new projects planned for the North Sea and Baltic Sea. It is anticipated that these projects will significantly boost Europe’s renewable energy capacity.
Additionally, significant investments are being made in electrifying transportation networks, including the construction of charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) and the expansion of high-speed rail networks.
Green infrastructure projects, such as the construction of energy-efficient buildings, sustainable urban drainage systems, and green spaces, are on the rise throughout Europe’s urban areas.
Long-Term Advantages:
These initiatives are essential for lowering Europe’s carbon footprint, improving air quality, and strengthening cities’ climate change resilience.
Europe is expected to become a global leader in sustainable development and create jobs as a result of the focus on green infrastructure.
3. India’s Infrastructure Modernization

India is undergoing a significant effort to modernize its infrastructure, including investments in digital infrastructure, energy, and transportation.
Recent Projects:
The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) has been launched by the Indian government. This multi-year plan aims to develop over 7,000 projects in various fields, such as roads, railways, and urban infrastructure.
The Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train and other high-speed rail projects are moving forward with significant technological and financial support from Japan.
India is also putting a lot of emphasis on expanding its digital infrastructure, with projects aimed at increasing rural broadband connectivity and building smart cities with cutting-edge technology.
Strategic Value:
India’s economic growth, regional disparities, and global competitiveness are all dependent on these infrastructure projects.
In addition, modernizing infrastructure is essential for attracting foreign investment, enhancing citizens’ quality of life, and supporting the country’s efforts at industrialization and urbanization.
Global Infrastructure: New Trends 1. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) Are Increasing Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) are Increasingly used to finance and carry out global large-scale infrastructure projects by utilizing the expertise and investment of the private sector.
Recent instances:
PPPs are being used to build major infrastructure projects in Latin America, such as highways, airports, and energy facilities, in countries like Brazil and Mexico.
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 plan for the Middle East includes a number of PPP-based projects that aim to diversify the economy by focusing on infrastructure for transportation, energy, and tourism.
PPPs are also growing in Africa, with projects ranging from renewable energy plants to water supply systems.
Challenges and Benefits:
PPPs are a way to get private capital for public infrastructure, save money for the government, and make projects run better.
However, in order to guarantee long-term viability and public benefit, successful PPPs require robust regulatory frameworks, precise risk-sharing arrangements, and efficient management.
4. The integration of smart technologies

Into infrastructure is transforming the design, construction, and operation of projects, with an emphasis on increasing connectivity, sustainability, and efficiency.
Important Changes:
Projects integrating IoT (Internet of Things) devices, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to manage urban services like traffic, energy, and waste are becoming a major focus of infrastructure development in smart cities.
The development of smart grids is accelerating, making it possible to better integrate renewable energy sources and distribute energy in a more effective manner.
Asset performance is being monitored and improved through the use of digital twins, which are virtual replicas of actual infrastructure. These assets range from railways and power plants to bridges and tunnels.
Impact on the World:
It is anticipated that cities and infrastructure networks will become more resilient as a result of the adoption of smart infrastructure, which will also reduce operational expenses and enhance the quality of services offered to citizens.
Cybersecurity measures to safeguard critical infrastructure from cyber threats are becoming increasingly important as nations invest in digital transformation.
5. Financing of Sustainable Infrastructure

An increasing focus on aligning infrastructure investments with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria is driving sustainable infrastructure financing.
Trends of Late:
Governments and businesses are issuing bonds to fund climate-resilient infrastructure, sustainable transportation, and renewable energy, making green bonds a popular way to finance sustainable infrastructure projects.
Projects that contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations are getting more attention from development banks like the World Bank and the Asian Development Bank.
Confidential financial backers are likewise progressively keen on foundation projects that fulfill ESG guidelines, driven by the developing interest for dependable speculation choices.
Opportunities and Challenges:
While sustainable financing presents significant opportunities, ensuring that projects are truly long-lasting and profitable presents challenges.
For sustainable infrastructure investments to remain credible, they must adhere to clear standards, transparent reporting, and stringent evaluation criteria.
In conclusion,
Global infrastructure projects are addressing the world’s most pressing issues, such as climate change and digital transformation to economic growth and urbanization. The importance of sustainability, innovation, and international cooperation is growing as nations make investments in building and upgrading their infrastructure. Not only do these projects help the economy grow, but they also help societies thrive and keep the planet for future generations. Stay tuned for more information about the most recent developments in worldwide infrastructure projects.



