Global health initiatives play a crucial role in improving public health outcomes, preventing disease, and ensuring access to essential healthcare services in a world that is becoming increasingly interconnected by shared health challenges. These initiatives, which are driven by governments, international organizations, and non-governmental organizations, address a wide range of health issues, including the prevention of infectious diseases and the enhancement of the health of mothers and children. This daily update sheds light on the most recent developments in global health initiatives, focusing on important projects, partnerships, and the ways in which these efforts have affected communities all over the world.
1. Global Distribution of Vaccines:
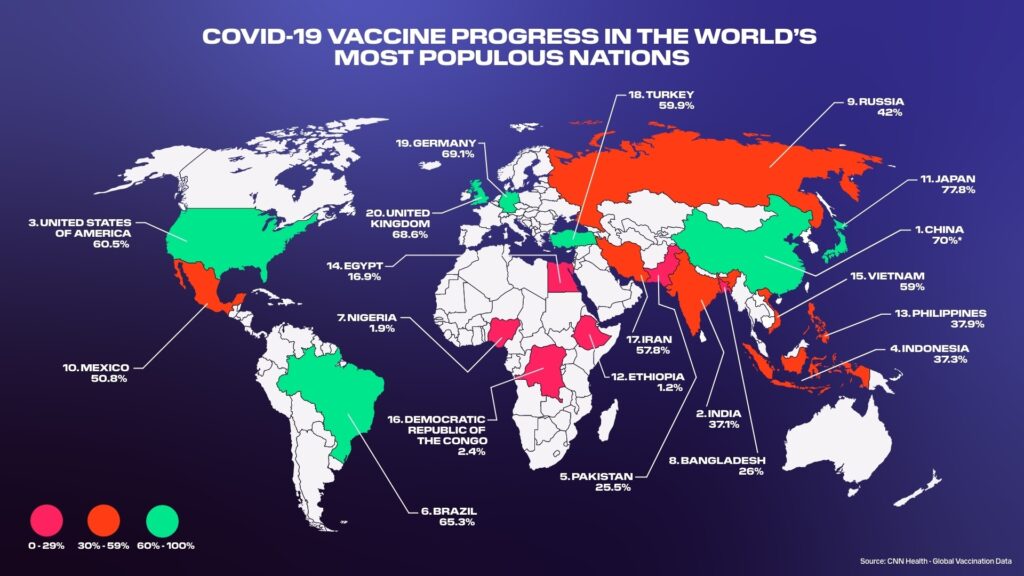
Increasing Access to Life-Saving Vaccinations Global efforts to increase vaccine access continue to be a top priority. Vaccination remains one of the most efficient public health tools for preventing infectious diseases.
Important Changes:
A new phase of the COVAX initiative has been launched by the World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). By the end of 2024, the goal of this phase is to give 500 million more doses of the COVID-19 vaccine to countries with low and middle incomes. Reaching out to rural and underserved areas where vaccine coverage is still low is the primary goal.
A continent-wide vaccination campaign against polio and measles has been led by the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) of the African Union. It is anticipated that this campaign, which is supported by UNICEF and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, will vaccinate 100 million children. Particular attention will be paid to countries where outbreaks are occurring as a result of a lack of routine immunization.
In Southeast Asia and Latin America, the expansion of HPV (human papillomavirus) vaccination programs is also making headlines. In an effort to prevent cervical and other HPV-related cancers, countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Indonesia are intensifying vaccination efforts for adolescents.
Impact on the World:
Controlling the spread of infectious diseases, protecting vulnerable populations, and moving closer to global health equity all depend on these vaccine distribution efforts. These initiatives contribute to the larger objective of eliminating diseases that can be avoided by ensuring that vaccines reach those who need them.
2. In the fight against non-communicable diseases (NCDs),

Strategies for Preventing and Treating Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) Non-communicable diseases include cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. Tending to NCDs requires a thorough methodology, and late worldwide wellbeing drives are centered around counteraction, early discovery, and the board.
Highlights of the Past:
A new global action plan has been launched by the WHO to cut the burden of noncommunicable diseases by 25% by 2030. The inclusion of NCD prevention in primary care, the promotion of healthy lifestyles, and improved access to early diagnosis and treatment are all emphasized in this plan. In addition, the plan encourages nations to implement policies that reduce risk factors like smoking, poor diet, and inactivity.
Large-scale diabetes screening and management programs have been implemented in South Asia by the governments of India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka in collaboration with the World Bank and the International Diabetes Federation. These programs aim to educate millions of people, particularly those living in rural areas, about how to change their lifestyles to avoid developing diabetes.
A regional effort to cut down on deaths caused by hypertension in the Americas has been launched by the American Heart Association and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO). In addition to raising public awareness of the significance of controlling blood pressure, the initiative also aims to improve access to affordable medications, train healthcare workers, and train the general public.
Results for health:
The incidence and impact of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are expected to decrease significantly as a result of these initiatives, thereby enhancing quality of life and lowering healthcare costs. Leaders in global health want to stem the rising tide of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) and promote healthier populations by focusing on prevention and management.
3. Health of Mothers and Children:

Improving maternal and child health is a central component of global health initiatives because healthy mothers and children are essential to the well-being of communities and societies. Strengthening Care for the Most Vulnerable
Important Projects:
“Every Child Alive,” a global initiative launched by UNICEF, aims to cut down on neonatal mortality by expanding access to high-quality maternal and newborn care. Over 80 countries are participating in the initiative, which focuses on providing mothers and babies with timely and effective care, enhancing facilities, and training healthcare workers.
The “Saving Mothers, Giving Life” initiative, which is supported by USAID and other partners in sub-Saharan Africa, is making significant progress in reducing maternal mortality. In order to improve the availability of skilled birth attendants, emergency obstetric care, and transportation for pregnant women in rural areas, the initiative collaborates with local governments.
Maternal and child health programs in low-income nations continue to receive crucial funding from the Global Financing Facility (GFF), a World Bank initiative. Improving nutrition, expanding vaccination coverage, and ensuring access to reproductive health services have all received recent grants.
Effects on Neighborhoods:
Communities’ overall health and development are benefiting from these maternal and child health initiatives, which are saving lives. These initiatives help break the cycle of poverty and poor health outcomes by focusing on the most vulnerable populations, paving the way for a healthier future.
4. Security for Global Health:

Strengthening Health Systems, Enhancing Disease Surveillance, and Preparing for Future Pandemics Following the COVID-19 pandemic, global health security has become a priority. These initiatives are focused on preparing for future pandemics.
Recent Events:
New initiatives to increase global preparedness for infectious disease outbreaks have been launched by the Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA), an international partnership comprised of over 70 nations. These include increasing the capacity of laboratories, training health professionals, and enhancing international data sharing.
A global pandemic preparedness fund has been established by the WHO, the World Bank, and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). The purpose of this fund is to assist nations in developing health systems that are resilient, enhancing vaccine research and development, and ensuring a prompt response to emerging health threats.
With assistance from international partners, nations in Southeast Asia like Thailand, Vietnam, and Malaysia are improving their public health infrastructure. Diagnostic laboratories are being upgraded, health worker training is being expanded, and community-based surveillance systems are being implemented as part of these efforts.
Long-Term Advantages:
In order to safeguard populations from future pandemics and other health emergencies, it is essential to enhance global health security. These initiatives assist in mitigating the effects of potential health crises and guarantee a prompt and efficient response by investing in resilience and preparedness.
5. Health mental:

Taking Care of a Global Crisis Mental health is becoming more and more recognized as an essential aspect of overall health, and numerous international initiatives are geared toward reducing the growing number of mental health disorders.
Important Changes:
The “Mental Health Gap Action Programme” (mhGAP) of the World Health Organization is expanding its reach by providing healthcare providers in low- and middle-income nations with training and resources. The program aims to make it easier for people to get the support they need by integrating mental health services into primary care.
A global campaign to reduce the stigma associated with mental health disorders has been launched by the United Nations, the World Bank, and the World Health Organization. The “Speak Your Mind” campaign promotes policies that support mental well-being and encourages open discussion about mental health.
The “European Framework for Action on Mental Health” has been implemented in Europe, focusing on preventing mental health disorders in young people, supporting mental health in the workplace, and improving mental health services. The larger effort to address the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and other social stressors on mental health includes this framework.
Impact on Society:
Mental health issues must be addressed if communities are to be resilient and healthy. These initiatives aim to lessen the burden of mental health disorders, make it easier for people with mental health issues to get care, and create a supportive environment.
In conclusion,
Global health initiatives are significantly advancing health outcomes, disease prevention, and universal access to essential healthcare services. These initiatives are essential to the creation of a world that is both healthier and more equitable. They include expanding access to vaccines, addressing non-communicable diseases, and strengthening health systems in preparation for potential pandemics. To comprehend their impact on global public health, it is essential to remain informed about these initiatives as global health challenges continue to evolve.



