A complicated logistical problem that has received a lot of attention since the COVID-19 pandemic. Successful dissemination methodologies are basic for guaranteeing that immunizations arrive at the people who need them in an opportune and impartial way. The COVID-19 vaccine rollout is the focus of this case study, which examines the planning, implementation, difficulties, and successes of various vaccine distribution methods.
Foundation and Setting
Significance of Immunization Appropriation:
Immunizations are a basic device in general wellbeing for forestalling irresistible sicknesses. Productive conveyance guarantees that antibodies are regulated generally and immediately, assisting with accomplishing group invulnerability and lessen illness transmission.
Coronavirus Immunization Advancement and Endorsement:
The quick turn of events and endorsement of Coronavirus immunizations addressed an exceptional logical accomplishment. The immunizations, created by organizations like Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Johnson and Johnson, were approved for crisis use in record time, requiring a quick and powerful circulation system.
Strategies for Vaccine Distribution Strategic Planning and Coordination:
Powerful immunization conveyance requires key preparation and coordination among different partners, including government organizations, medical care suppliers, and strategies organizations. Key components include:
Production network The executives: Guaranteeing the accessibility of antibodies, overseeing stock, and organizing transportation and capacity are vital for keeping up with the immunization production network.
Partner Coordination: A coordinated rollout necessitates cooperation from partners from the private sector as well as federal, state, and local authorities.
Case Study: In the US, Activity Twist Speed (OWS) was a government drive that organized immunization improvement, dissemination, and organization. The program included coordinated effort between the Division of Wellbeing and Human Administrations (HHS), the Branch of Safeguard (DoD), and confidential drug organizations.
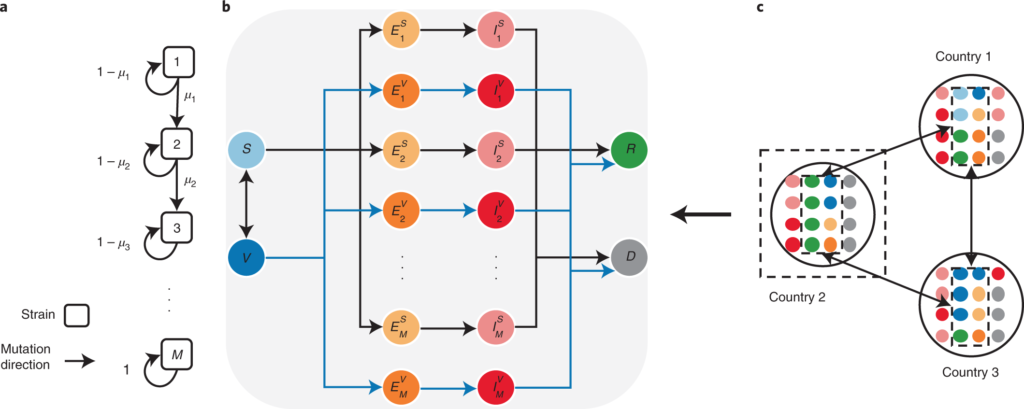
Logistics and channels of distribution:
Immunization dispersion includes different channels, including direct shipments to medical care suppliers, circulation focuses, and inoculation locales. Some important logistical considerations are:
Cold Chain Necessities: To remain effective, many COVID-19 vaccines must be stored at extreme temperatures. The cold chain, which includes specialized storage and transportation, needs to be managed well.
Distributor Systems: Using existing medical services foundation, like drug stores, clinics, and centers, works with effective immunization conveyance.
Case Study: The COVID-19 vaccine manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech must be stored at -70°C (-94°F). To ensure that the required temperature is maintained during transport, Pfizer designed custom shipping containers made of dry ice. The organization likewise settled associations with coordinated factors firms to guarantee opportune conveyance.
Allocation and Prioritization:
A crucial aspect of the distribution strategy is prioritizing the distribution of vaccines to various populations. Prioritization is normally founded on variables, for example, age, ailments, occupation, and chance of openness.
Phased Expansion: Immunization endeavors are many times executed in stages, beginning with high-risk gatherings like medical care laborers and the old, prior to extending to everybody.
Case Study: In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provided guidance on vaccine priority, recommending that vulnerable populations and frontline workers be vaccinated first.
Public Correspondence and Training:

Compelling correspondence and government funded training are urgent for empowering immunization take-up and tending to antibody aversion. These methods include:
Publicity campaigns: Building public trust and encouraging vaccination are both aided by providing clear, accurate information about vaccine benefits and safety.
Connecting with Local area Pioneers: Reaching out to a wide range of people and addressing issues can be made easier by collaborating with reputable community leaders and organizations.
Case Study: The Coronavirus inoculation crusade included public assistance declarations, web-based entertainment effort, and local area based drives to give data and counter falsehood.
Inoculation Destinations and Availability:
Reaching all populations requires establishing accessible vaccination sites and ensuring equitable distribution. Contemplations include:
Choosing a Location: Picking areas that are helpful and open for different populaces, including underserved networks.
Pop-Up and mobile clinics: Using portable facilities and impermanent immunization destinations can assist with contacting people who might experience issues getting to conventional inoculation locales.
Case Study: During the Coronavirus pandemic, numerous wards laid out mass immunization destinations, for example, arenas and assembly halls, and used portable inoculation units to arrive at remote and underserved regions.
Difficulties and Arrangements
Store network Interruptions:
The worldwide interest for immunizations and the intricacy of cold chain necessities presented difficulties in guaranteeing ideal and solid appropriation. Arrangements included:
Better Logistics: Putting resources into cutting edge operations and production network the executives innovations to follow and oversee antibody dissemination.
Cooperation with Accomplices: working on supply chain issues with pharmaceutical companies, logistics companies, and government agencies.
Value and Access:
Guaranteeing impartial admittance to immunizations, especially for underestimated and underserved networks, was a huge test. Arrangements included:
Designated Effort: targeting underserved populations by putting in place specialized outreach programs and forming partnerships with community organizations.
Transportation that is subsidized: assisting individuals in getting to vaccination sites by providing transportation assistance.
Vaccine aversion:
In order to achieve high vaccination rates, it was essential to address vaccine hesitancy and misinformation. Some solutions were:
Educational Programs: Creating designated instructive missions to address concerns and give precise data about immunization security and viability.
Relationships with Influencers: Collaborating with well known individuals and local area pioneers to advance immunization and counter deception.
Information The board and Following:
Proficiently following immunization dispersion, organization, and patient records is fundamental for guaranteeing inclusion and overseeing stock. Arrangements included:
Electronic Systems: using digital databases and tracking systems to keep an eye on vaccine distribution and administration in real time.
Integration with Medical Files: Incorporating immunization information with electronic wellbeing records to smooth out following and announcing.
Effect and Results
Immunization Inclusion:
In many areas, high vaccination coverage has been achieved through the implementation of efficient vaccine distribution strategies. As a result, transmission rates have decreased, severe illness incidence has decreased, and progress toward herd immunity has been made.
General Wellbeing Enhancements:
The widespread vaccination of people has been crucial to halting the spread of COVID-19, reducing the number of people hospitalized, and saving lives. The effectiveness of distribution strategies in managing crises involving public health has been demonstrated by the vaccine’s successful rollout.
Examples Learned:
The COVID-19 vaccine rollout has taught us a lot about how to distribute vaccines and respond to public health issues. These examples will illuminate future inoculation endeavors and pandemic readiness.
Future Headings
Fortifying Stockpile Chains:
For subsequent vaccination campaigns and responses to pandemics, it will be essential to maintain investment in the logistics and infrastructure of the vaccine supply chain.
Upgrading Value:
In order to reduce health disparities and improve public health outcomes, ongoing efforts to ensure equitable access to vaccines and healthcare will be necessary.
Advancements in Dispersion:
Progressions in innovation and conveyance strategies, for example, advanced wellbeing records and further developed cold chain arrangements, will improve the productivity and viability of antibody dissemination.
State funded Training and Commitment:
Supported endeavors to teach general society and address antibody reluctance will stay significant for keeping up with high inoculation rates and guaranteeing fruitful general wellbeing drives.
End
The Coronavirus antibody dissemination exertion has featured the basic significance of key preparation, coordination, and advancement in tending to general wellbeing challenges. Successful dispersion systems have empowered far reaching immunization inclusion, adding to the control of the pandemic and working on general wellbeing. The illustrations gained from this experience will keep on molding future immunization endeavors and general wellbeing reactions, highlighting the requirement for progressing interest in framework, value, and training.



