Man-made brainpower (artificial intelligence) is reforming different areas, and medical care is no exemption. In diagnostics, computer based intelligence is ending up a groundbreaking device that improves exactness, speeds up processes, and might possibly lessen medical care costs. This contextual analysis analyzes the job of simulated intelligence in diagnostics, investigating its applications, advantages, difficulties, and future headings.
Foundation and Setting
The Requirement for Cutting edge Diagnostics:
Precise and ideal analysis is essential for compelling treatment and the board of illnesses. Customary symptomatic strategies, while successful, frequently face limits concerning rate, precision, and versatility. Man-made intelligence offers additional opportunities by utilizing progressed calculations and information investigation to work on symptomatic cycles.
Technology advancements in AI:
Artificial intelligence advances, including AI (ML) and profound learning, have seen huge progressions as of late. These innovations can dissect huge datasets, distinguish examples, and make expectations with expanding accuracy. In diagnostics, man-made intelligence frameworks are prepared on huge measures of clinical information to perceive illnesses and peculiarities.
Utilizations of computer based intelligence in Diagnostics
Clinical Imaging:
In the analysis of medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, AI has demonstrated remarkable success. Computer based intelligence calculations can recognize irregularities and help radiologists in deciphering pictures all the more precisely.
Case Study: IBM’s Watson for Wellbeing has been utilized to investigate clinical pictures for different circumstances, including disease and neurological issues. In a review including bosom disease identification, man-made intelligence calculations showed similar or better exactness looked at than radiologists in recognizing harmful growths.
Pathology:
In pathology, computer based intelligence helps with analyzing tissue tests and distinguishing cell irregularities. Man-made intelligence calculations can dissect slides to identify harmful cells and other obsessive circumstances.
Case Study: PathAI, a simulated intelligence organization, creates calculations to help pathologists in diagnosing malignant growth and different sicknesses. Their simulated intelligence models have been displayed to work on analytic exactness and diminish changeability among pathologists.
Genomics:
Computer based intelligence assumes a critical part in genomics by dissecting hereditary information to recognize transformations and foresee illness risk. Artificial intelligence devices can handle huge scope genomic information to give experiences into hereditary issues and customized treatment choices.
Case Study: Google’s DeepMind has applied man-made intelligence to genomic research, especially in understanding protein collapsing. This examination has suggestions for diagnosing hereditary illnesses and creating designated treatments.
Prescient Investigation:
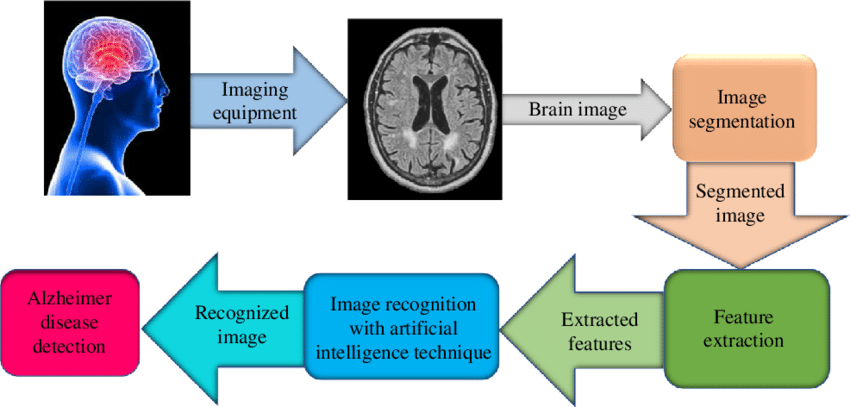
Man-made intelligence models can investigate patient information to foresee illness chance and results. By coordinating electronic wellbeing records (EHRs) and different information sources, simulated intelligence can distinguish patients in danger for conditions like diabetes, coronary illness, and disease.
Case Study: Wellbeing frameworks use artificial intelligence controlled prescient examination to recognize patients at high gamble of readmission or crumbling. AI algorithms, for instance, look at patient data to predict sepsis and allow for early intervention.
Diagnostics in the Laboratory:

Through the automation and optimization of various tests and analyses, AI improves laboratory diagnostics. Man-made intelligence frameworks can work on the exactness and proficiency of blood tests, pee tests, and other indicative measures.
Case Study: An AI platform that aids radiologists in analyzing CT scans and determining critical conditions is offered by the company Aidoc. The stage gives ongoing alarms to earnest cases, upgrading analytic effectiveness.
Advantages of artificial intelligence in Diagnostics
Expanded Precision:
Artificial intelligence calculations, prepared on enormous datasets, can distinguish examples and inconsistencies with high accuracy. Diagnostic errors can be reduced and diagnostic accuracy can be improved as a result.
Efficiency and rapidity:
Traditional methods take much longer to process and analyze medical data than AI systems can. This speed is especially gainful in high-volume demonstrative settings, where convenient outcomes are vital.
Scalability:
Across a variety of healthcare settings, AI tools can be scaled to handle large amounts of data and provide consistent diagnostic support. In underserved and remote areas, this scalability can improve diagnostic capabilities.
Customized Medication:

By examining individual patient information, simulated intelligence can add to customized medication, giving custom-made treatment proposals in view of explicit patient attributes and hereditary data.
Reduced Costs:
Computer based intelligence might possibly decrease analytic costs by further developing proficiency, diminishing the requirement for rehash tests, and smoothing out symptomatic work processes.
Difficulties and Contemplations
Information Quality and Predisposition:
The quantity and quality of the training data are crucial to AI’s diagnostic efficiency. Predispositions in information can prompt wrong or inconsistent analytic results, especially for underrepresented populaces.
Ethical and regulatory issues:
The coordination of artificial intelligence into diagnostics raises administrative and moral worries, including issues connected with information security, calculation straightforwardness, and the requirement for approval and certificate of man-made intelligence apparatuses.
Coordination with Existing Frameworks:
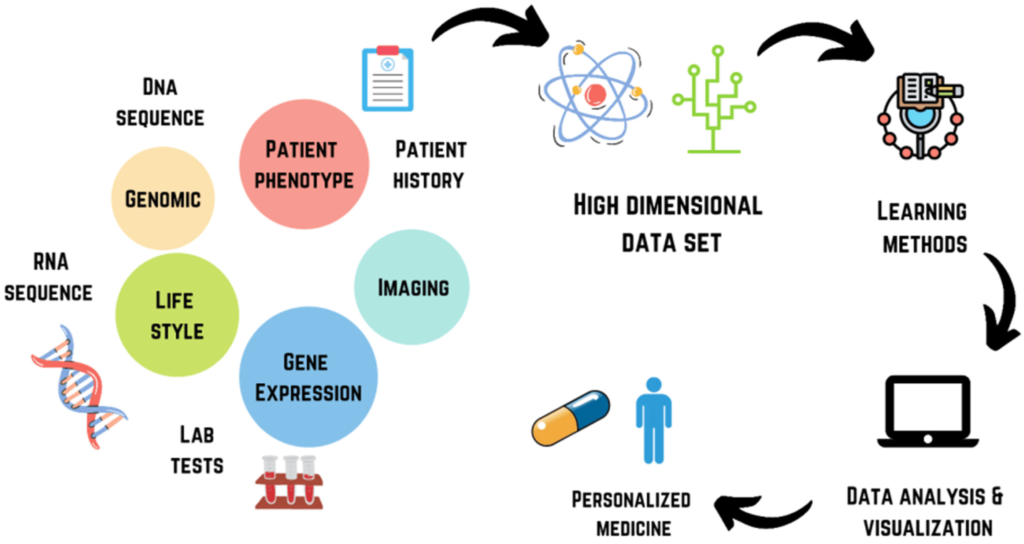
Coordinating artificial intelligence frameworks with existing medical services foundation, like EHRs and symptomatic hardware, can be mind boggling. Successful mix requires interoperability and coordinated effort among innovation suppliers and medical care establishments.
Human Control:
Although AI can improve diagnostic procedures, human oversight is still necessary. The expertise of healthcare professionals should be complemented, not substituted, by AI systems. Guaranteeing that artificial intelligence apparatuses are utilized fittingly and successfully requires continuous preparation and joint effort.
Implementation Cost:
The turn of events and execution of artificial intelligence frameworks can be expensive. Medical care associations should consider the monetary venture expected for computer based intelligence innovation and weigh it against possible advantages and investment funds.
AI Algorithm Developments in the Future:

Proceeded with innovative work will prompt further developed artificial intelligence calculations equipped for taking care of perplexing indicative undertakings and further developing precision. Developments in profound learning and brain organizations will drive further advancement.
Improved Information Combination:
Future computer based intelligence frameworks will profit from further developed coordination of different information sources, including genomics, clinical imaging, and patient records. This joining will empower more thorough and exact diagnostics.
Getting Rid of Inequality and Bias:
Endeavors to address information inclination and guarantee evenhanded admittance to artificial intelligence symptomatic devices will be pivotal for accomplishing fair and precise results across various populaces.
Administrative Structures:
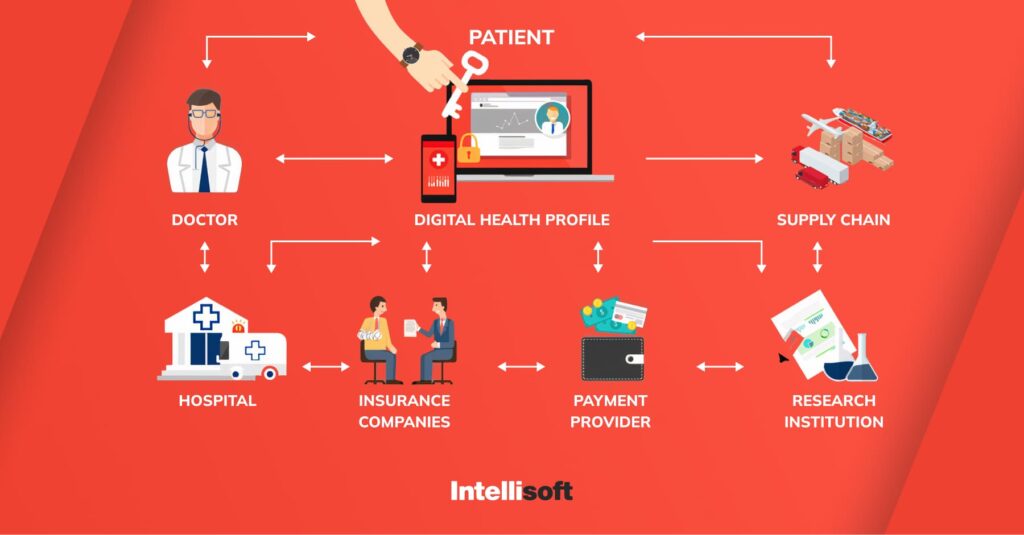
Growing clear administrative systems for computer based intelligence in diagnostics will be significant for guaranteeing the security, adequacy, and moral utilization of artificial intelligence devices. Cooperation between controllers, medical services suppliers, and innovation engineers will be vital.
Education and Training:
Continuous preparation and training for medical care experts will be fundamental for actually incorporating computer based intelligence into analytic work processes. Guaranteeing that experts are know about man-made intelligence devices and their applications will improve the general effect of man-made intelligence in medical care.
End
Computer based intelligence is assuming a groundbreaking part in diagnostics, offering huge upgrades in precision, speed, and proficiency. The combination of man-made intelligence into indicative cycles can possibly improve patient consideration, support customized medication, and lessen medical care costs. In any case, tending to difficulties like information quality, administrative issues, and combination intricacies is fundamental for understanding the maximum capacity of artificial intelligence in diagnostics. As innovation keeps on propelling, artificial intelligence will probably turn into an inexorably fundamental part of symptomatic works on, forming the fate of medical care.



