The quick turn of events and sending of the Coronavirus immunization by Pfizer-BioNTech denoted a noteworthy accomplishment in drug development and general wellbeing. One of the first COVID-19 vaccines to receive Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from regulatory agencies all over the world was the vaccine, which is officially known as BNT162b2. The scientific, regulatory, and logistical obstacles overcome during the COVID-19 vaccine development by Pfizer are the focus of this case study.
Context and Background of the COVID-19 Pandemic:
Beginning in the early months of 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 virus was the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a global health crisis. States, medical care frameworks, and scientists overall confronted exceptional difficulties in dealing with the pandemic and looking for successful arrangements.
Imperative for Vaccine Development:
To control the virus’s spread and lessen the effects of the pandemic, it became a top priority to develop a vaccine that was both safe and effective. The desperation of the circumstance sped up immunization innovative work endeavors across the globe.
Pfizer’s Collaboration with BioNTech on the Process of Developing Vaccines:

Pfizer, a main drug organization, joined forces with BioNTech, a German biotechnology firm work in mRNA innovation, to foster a Coronavirus immunization. This cooperation utilized BioNTech’s mastery in mRNA antibodies and Pfizer’s involvement with immunization improvement and circulation.
Case Study: BNT162b2, an mRNA-based vaccine designed to elicit an immune response against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, was developed as a result of the collaboration.
Innovative work:
Preclinical Research: Pfizer and BioNTech started by directing preclinical examinations to assess the security and viability of the antibody in creature models. The mRNA innovation, which utilizes hereditary material to train cells to deliver a protein that gets an insusceptible reaction, was a clever methodology for immunization improvement.
Clinical Preliminaries: The immunization went through a progression of clinical preliminaries in stages:
Stage 1/2 Preliminaries: These preliminaries evaluated the security, bearableness, and primer viability of the immunization in a little gathering of sound workers. Introductory outcomes showed areas of strength for a reaction and hardly any unfriendly impacts.
Stage 3 Preliminaries: Phase 3 trials evaluated the vaccine’s safety profile and efficacy in preventing COVID-19 infection with tens of thousands of participants. The trials showed that the vaccine was 95 percent effective at preventing COVID-19 infection with symptoms.
Case Study: The New England Journal of Medicine published the Phase 3 trials’ findings, which demonstrated that BNT162b2 had a favorable safety profile and offered robust protection against COVID-19.
Administrative Endorsement and Crisis Use Approval:
Submissions to the Regulator: Pfizer and BioNTech presented regulatory agencies with clinical trial data for evaluation. The vaccine was granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of the United States in addition to similar approvals from regulatory agencies in other nations, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Case Study: The FDA granted EUA to BNT162b2 on December 11, 2020, marking a significant turning point in the fight against COVID-19. This approval considered the immunization’s dispersion and organization to general society under unambiguous circumstances.
Distribution and Production:
Increasing Creation: Pfizer and BioNTech quickly increased immunization creation to satisfy worldwide need. For the vaccine to be consistent and effective, the manufacturing process required sophisticated technology and stringent quality control measures.
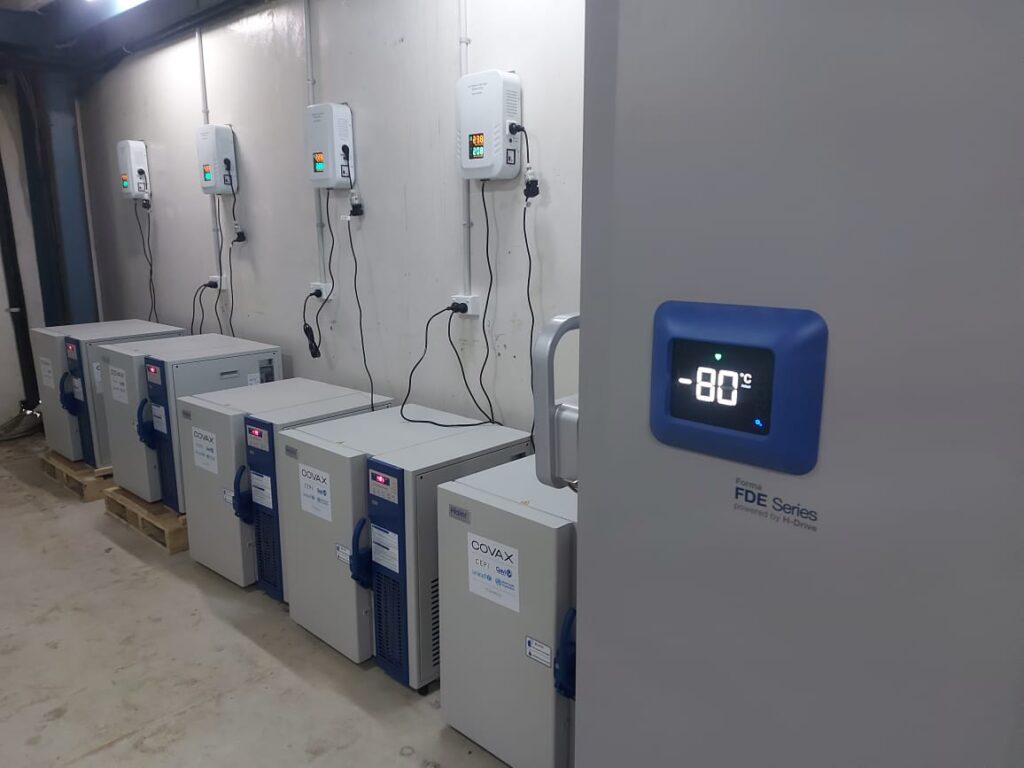
Logistics for Cold Chains: BNT162b2 required ultra-low temperatures (-70°C or -94°F) for storage, which presented logistical difficulties. Pfizer created specific steel trailers with dry ice to keep up with the vital temperature during transportation.
Case Study: In order to deliver the vaccine to various regions, Pfizer established a global distribution network. The organization teamed up with planned operations accomplices and utilized progressed global positioning frameworks to guarantee convenient and secure conveyance.
Application of Vaccines:
Introductory Conveyance: The immunization was at first circulated to high-need gatherings, including medical services laborers, old people, and those with hidden ailments. In order to guarantee equitable access, the rollout was coordinated with governments and public health agencies.
Communication with Others: Pfizer and BioNTech collaborated on public education campaigns to address vaccine safety and efficacy concerns and increase vaccination rates.
Case Study: In the U.S., the Habitats for Infectious prevention and Anticipation (CDC) and state wellbeing offices worked with Pfizer to lay out immunization destinations and regulate the antibody to qualified people.
Manufacturing and the Supply Chain: Challenges and Solutions:

Challenge: Increasing creation to fulfill worldwide need while guaranteeing quality control and keeping up with cold chain prerequisites.
Solution: Pfizer put resources into cutting edge fabricating innovation, enhanced creation processes, and laid out a worldwide production network organization. The organization likewise teamed up with different makers to increment creation limit.
Administrative Obstacles:
Challenge: Exploring the administrative endorsement process for another antibody under crisis conditions.
Solution: Pfizer and BioNTech worked intimately with administrative organizations to give far reaching information and address any worries. The sped up survey process was worked with by the pressing requirement for a Coronavirus immunization.
Public Insight and Immunization Aversion:
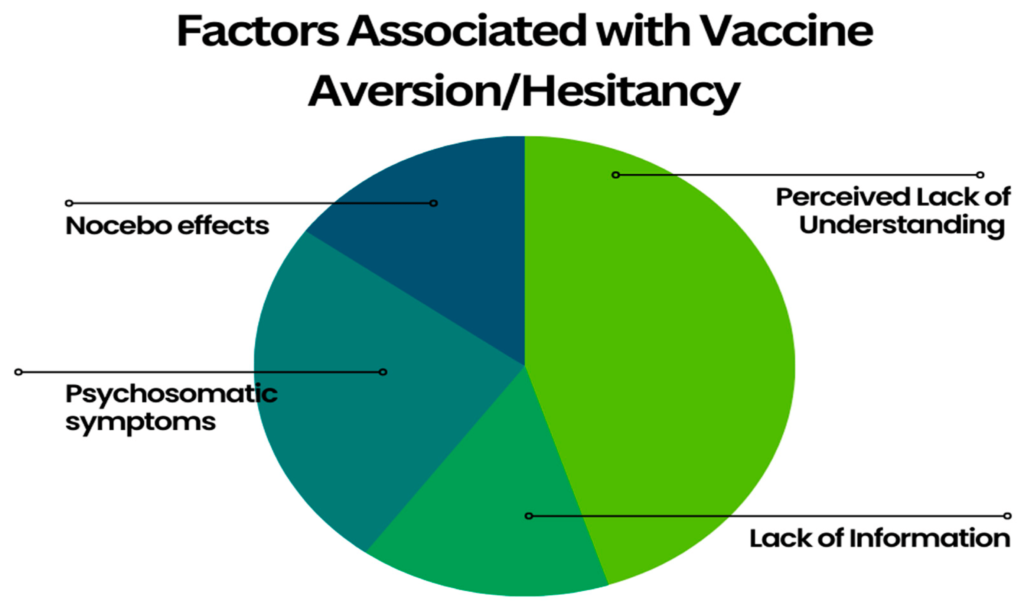
Challenge: Tending to public worries and falsehood about the new immunization.
Solution: Pfizer and BioNTech led instructive missions, drew in with medical services experts, and gave straightforward data about the immunization’s turn of events, security, and viability.
Evenhanded Dispersion:
Challenge: Guaranteeing fair and impartial admittance to the antibody, especially in underserved and low-pay networks.
Solution: Pfizer and BioNTech teamed up with legislatures and non-administrative associations to help immunization endeavors in underserved regions and address conveyance challenges.
Effect and Results

General Wellbeing Effect:
The presentation of the Pfizer-BioNTech Coronavirus immunization significantly affects worldwide general wellbeing. The immunization has added to a huge decrease in Coronavirus cases, hospitalizations, and passings.
Worldwide Immunization Endeavors:
The global vaccination campaign against COVID-19 has relied heavily on the vaccine, which has been given to millions of people all over the world. Its accessibility has upheld endeavors to accomplish crowd invulnerability and control the spread of the infection.
Perspectives for Future Innovation:
The progress of the Pfizer-BioNTech antibody has shown the capability of mRNA innovation for future immunization advancement. The innovation could be applied to other irresistible infections and remedial regions.
Future Headings

Progressing Exploration:
For maintaining effective protection against COVID-19, ongoing research on the vaccine’s long-term efficacy, booster doses, and adaptations to emerging virus variants will be necessary.
Global Equity in Vaccines:
Priority will continue to be given to ensuring equitable vaccine access, particularly in low-income and underserved regions. It will be essential to take steps to support global vaccination efforts and reduce disparities.
Technology Developments:

Progressions in antibody innovation, assembling, and dissemination will keep on upgrading the turn of events and sending of future immunizations. Public health will benefit from advancements in mRNA technology and other methods.
General Wellbeing Readiness:
Examples gained from the Coronavirus antibody advancement and rollout will illuminate future general wellbeing readiness and reaction methodologies for pandemics and other wellbeing crises.
End
Pfizer’s improvement of the Coronavirus immunization addresses a milestone accomplishment in drug development and general wellbeing. The fight against COVID-19 has been transformed as a result of the effective distribution and rollout, rapid development and regulatory approval, and fruitful collaboration with BioNTech. The lessons learned from this endeavor will guide the creation of new vaccines and global health strategies in the future, highlighting the significance of creativity, teamwork, and perseverance in addressing public health issues.



