The field of health and medicine is experiencing unprecedented advancements, thanks to rapid technological progress, groundbreaking research, and innovative treatment methods. These medical breakthroughs are transforming the way we understand, diagnose, and treat various health conditions, ultimately enhancing the quality of life and longevity for people around the world. Here, we explore some of the most significant health and medical breakthroughs that are shaping the future of healthcare.
1. Genomic Medicine and Personalized Healthcare

Genomic Sequencing: The completion of the Human Genome Project has opened up new avenues in genomic medicine. Advances in genomic sequencing technology have made it possible to decode an individual’s entire genome quickly and affordably. This capability is paving the way for personalized medicine, where treatments and preventive measures are tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
CRISPR and Gene Editing: The CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology has revolutionized genetic research by allowing precise modifications to DNA. This technology holds promise for curing genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia, by directly correcting the underlying genetic mutations.
2. Immunotherapy and Cancer Treatment
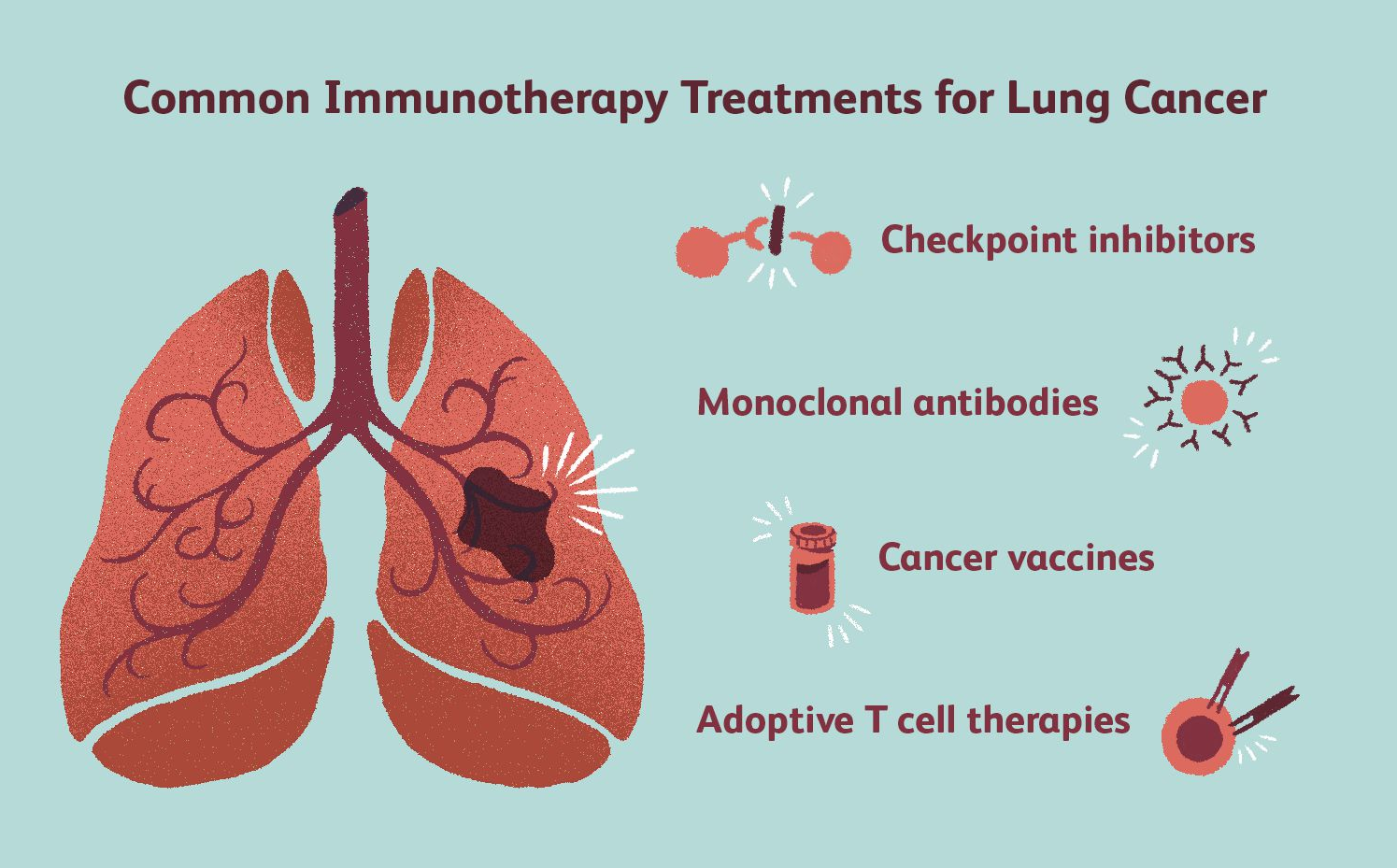
Checkpoint Inhibitors: Immunotherapy has emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against cancer. Checkpoint inhibitors, a type of immunotherapy, work by blocking proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. This approach has shown remarkable success in treating various cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and lymphoma.
CAR-T Cell Therapy: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy involves modifying a patient’s T-cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. This personalized treatment has demonstrated high efficacy in treating certain types of blood cancers, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
3. Advancements in Neurology and Mental Health

Neurostimulation: Neurostimulation techniques, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), are being used to treat neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and depression. These methods involve using electrical or magnetic impulses to stimulate specific brain regions, alleviating symptoms and improving patient outcomes.
Psilocybin Therapy: Emerging research on psychedelic compounds like psilocybin, found in magic mushrooms, suggests they have therapeutic potential for treating mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Clinical trials are ongoing to better understand the efficacy and safety of these treatments.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Digital Health

AI Diagnostics: Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming diagnostics by enabling faster and more accurate interpretation of medical images and data. AI algorithms can detect patterns and anomalies in radiology scans, pathology slides, and genetic data, assisting healthcare professionals in early diagnosis and treatment planning.
Telemedicine: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, allowing patients to receive medical consultations and care remotely. This shift has improved access to healthcare, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas, and has proven to be a convenient and effective mode of care delivery.
5. Regenerative Medicine and Organ Transplants
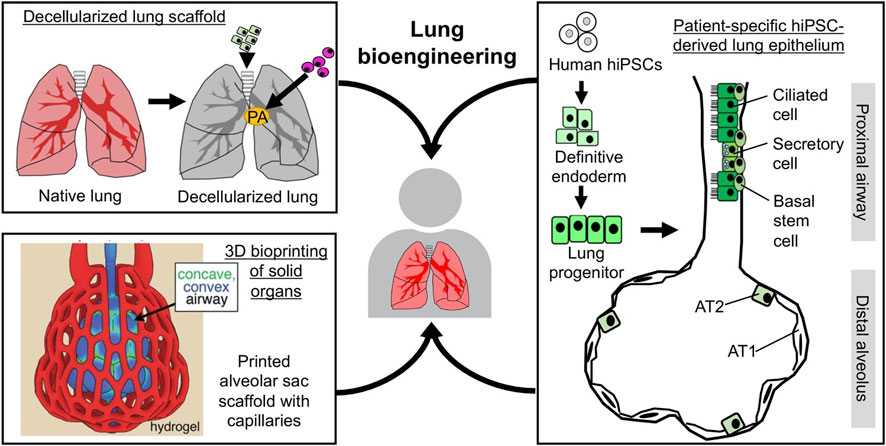
Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell research is advancing the field of regenerative medicine, offering potential treatments for conditions such as spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and diabetes. Stem cell therapy involves using undifferentiated cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs, promoting healing and regeneration.
3D-Printed Organs: The development of 3D bioprinting technology is making it possible to create custom tissues and organs for transplantation. Researchers are working on printing complex structures like blood vessels, skin, and even entire organs, which could address the critical shortage of donor organs and save countless lives.
6. Infectious Disease Control and Vaccination
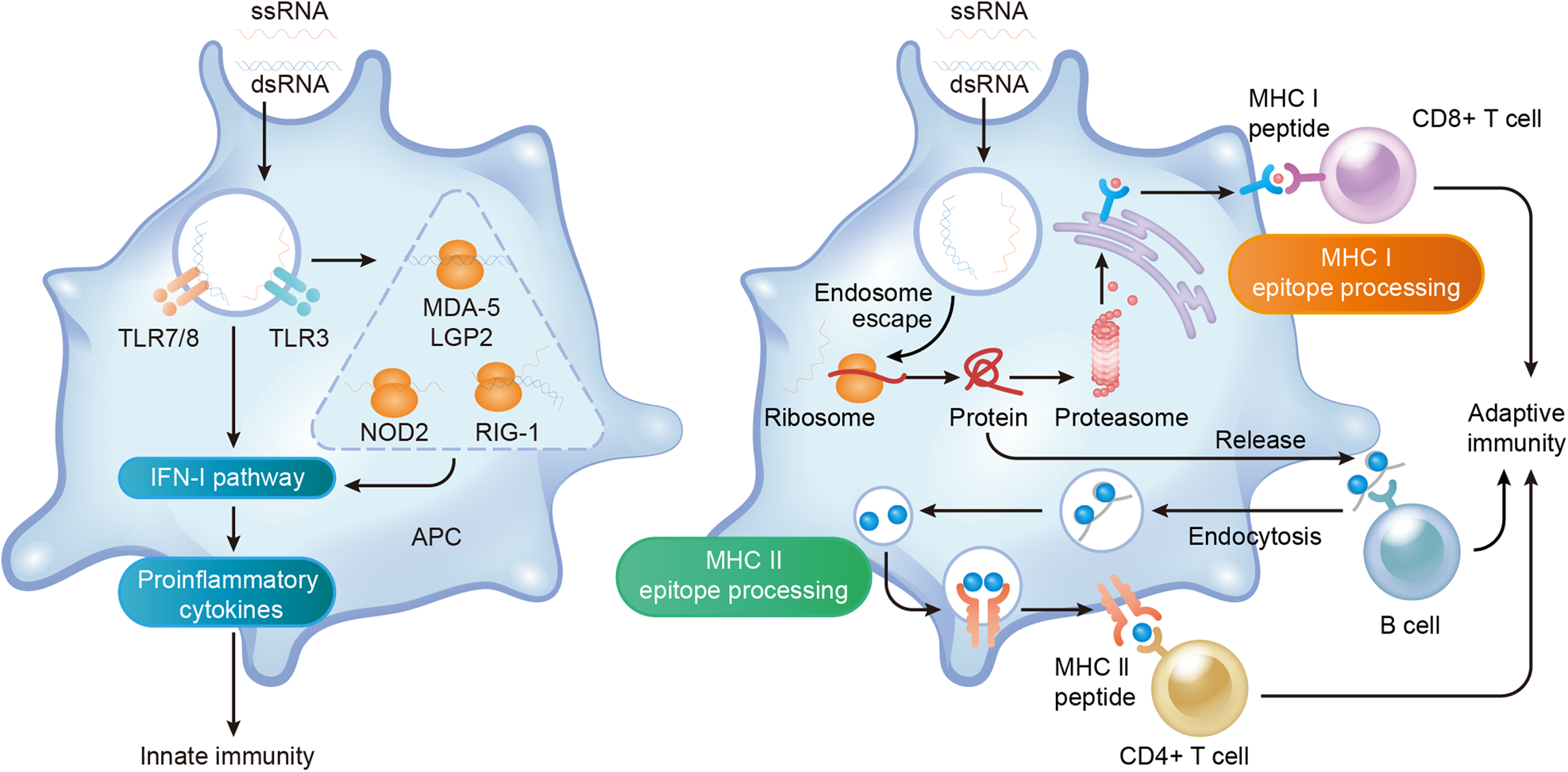
mRNA Vaccines: The rapid development and deployment of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19, such as those by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, represent a major breakthrough in vaccine technology. mRNA vaccines can be developed quickly and offer high efficacy, revolutionizing the way we respond to infectious disease outbreaks.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Efforts to combat antimicrobial resistance are advancing, with new antibiotics and alternative treatments being researched. Phage therapy, which uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to target drug-resistant bacteria, is one promising approach under investigation.
Conclusion
The landscape of health and medicine is continually evolving, driven by relentless innovation and scientific discovery. These medical breakthroughs hold the potential to not only treat and cure diseases but also to prevent them, ultimately leading to a healthier and longer life for individuals worldwide. As research and technology advance, the future of healthcare looks promising, with the potential to achieve unprecedented levels of personalized, effective, and accessible medical care.




