Space exploration has entered a new era, with private companies and government space agencies making significant progress toward improving our comprehension of the cosmos. The global push to explore and use space is accelerating, from pioneering Space Missions to far-off planets and moons to the creation of new space technologies. This daily update highlights key developments, challenges, and the potential impact on humanity’s future in space, highlighting the most recent news and breakthroughs in worldwide space missions.
Important Changes in Space Missions
1. The Artemis Program of NASA:
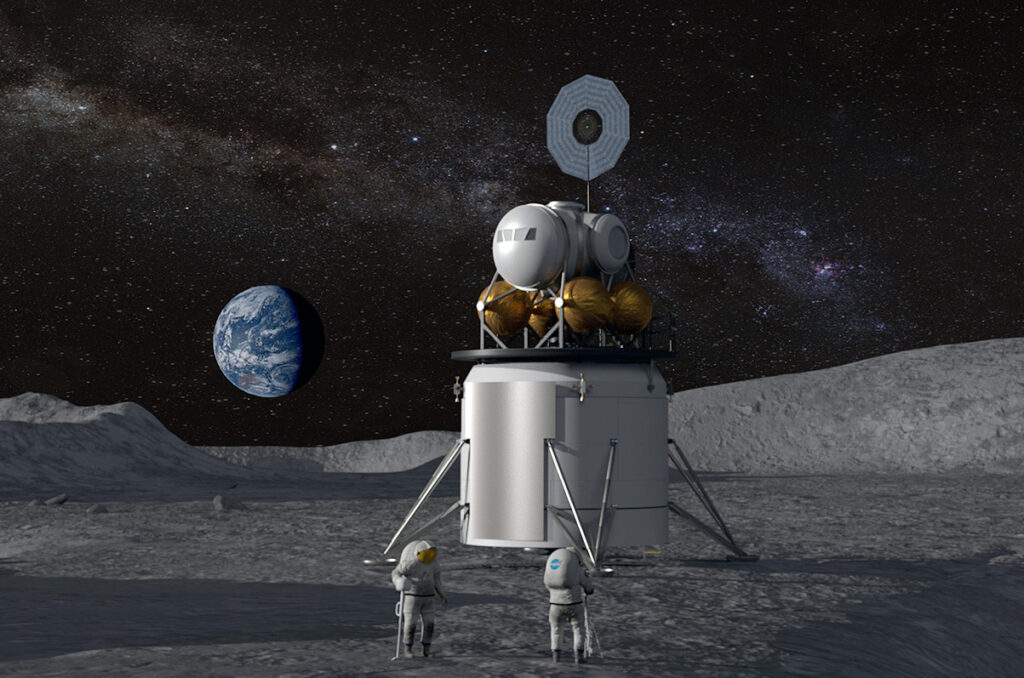
Paving the Way for Lunar Exploration The ambitious plans of NASA’s Artemis program to bring humans back to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence there keep it at the forefront of global space exploration efforts.
Late Achievements:
The first woman and the next man are expected to arrive on the lunar surface during the Artemis III mission, which is scheduled for late 2024. The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft have been put through their final tests as part of NASA’s final preparations.
NASA has chosen landing spots close to the South Pole of the moon where the presence of water ice could provide essential resources for subsequent missions. Both scientific research and the potential construction of a lunar base would benefit greatly from visiting these locations.
The improvement of the Door, a lunar circling station that will uphold missions to the Moon and then some, is advancing. Global accomplices, including the European Space Organization (ESA), Japan’s JAXA, and Canada’s CSA, are contributing key parts to this venture.
Future Objectives and Challenges:
The Artemis program is moving forward, but it faces a lot of obstacles, like a limited budget, technical obstacles, and the need for constant political support.
Preparing for human missions to Mars, Artemis’s ultimate objective is to use the Moon as a stepping stone for deep space exploration. Future Mars missions will benefit greatly from the lessons learned from previous missions.
2. Exploration of Mars:
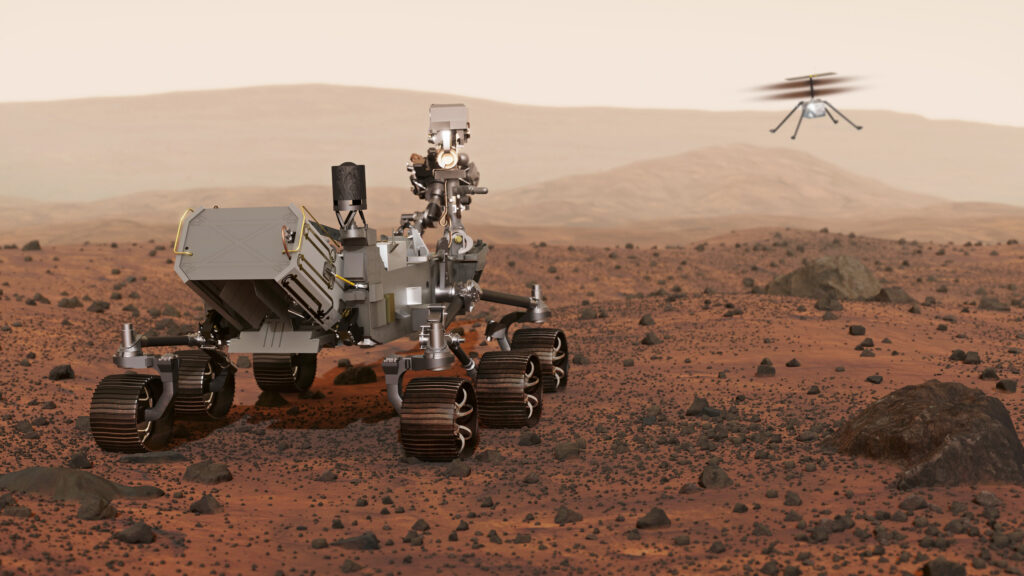

Space agencies and private businesses alike continue to be captivated by the Global Race to the Red Planet Mars, with a number of missions currently exploring the planet and more planned for the near future.
Continuous Missions:
The collection of soil and rock samples that will be brought back to Earth on a subsequent mission is one of the groundbreaking scientific investigations that NASA’s Perseverance rover is carrying out on Mars. Ingenuity, the rover’s helicopter, has also been making historic flights, demonstrating the possibility of space travel.
Another significant accomplishment is China’s Tianwen-1 mission, which consists of an orbiter, lander, and rover. The Zhurong rover has been exploring the surface of Mars, collecting useful information about the planet’s climate and geology.
The Hope Mars Mission, which is studying the Martian atmosphere and weather patterns, is still in operation by the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The dynamics of the planet’s climate are now better understood thanks to this mission.
Coming Assignments:
The ExoMars rover’s launch, which has been rescheduled for 2026, is being planned by the European Space Agency (ESA) and Roscosmos, Russia. The mission aims to look for evidence of past life on Mars.
The ambitious Starship project that SpaceX is working on to get humans to Mars is moving along. SpaceX continues to test and improve its spacecraft despite the uncertainty surrounding the timeline for a crewed Mars mission.
Consequences for the Future:
Mars investigation isn’t just about logical revelation; Additionally, it serves as a test bed for the strategies and technologies required for future human missions. The outcome of these missions will be vital for humankind’s drawn out objective of turning into a multi-planetary animal types.
3. Global Joint effort in Space Investigation
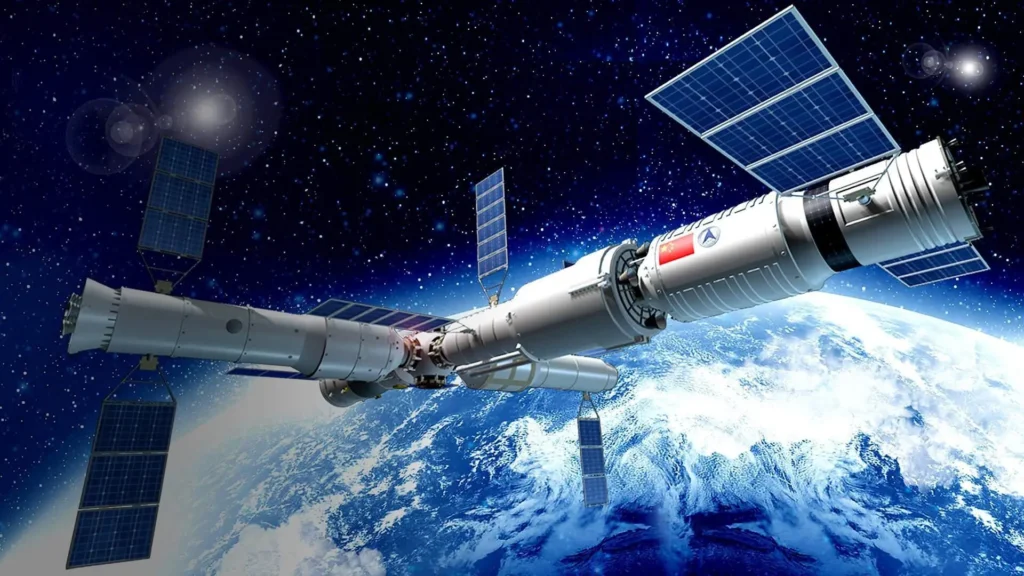

Worldwide participation stays a foundation of room investigation, with nations progressively cooperating on aggressive missions and ventures.
Recent Efforts to Work Together:
With astronauts from the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada conducting research in microgravity, the International Space Station (ISS) remains a symbol of international cooperation. It is anticipated that the ISS will continue to operate until at least 2030, and there are currently discussions taking place regarding its eventual demise and possible replacements.
Another illustration of international collaboration is the Lunar Gateway project, which is part of NASA’s Artemis program and involves contributions from international space agencies. It is anticipated that this partnership will open the door to more in-depth space exploration and enhance international space cooperation.
India and Japan have announced plans to work together on a joint lunar mission that will explore the Moon’s surface with a lander and rover. This mission, expected to send off in 2025, will additionally reinforce ties between the two spacefaring countries.
Advantages and Difficulties:
Countries can pool resources, share expertise, and achieve more ambitious objectives through international collaboration in space exploration than they could on their own. It likewise advances harmony and understanding among countries through shared logical undertakings.
In any case, international pressures can at times strain these coordinated efforts. The global community faces a challenge that must be carefully navigated in order to ensure that space remains a space for peaceful exploration and cooperation.
4. The Job of Privately owned businesses in Space Investigation
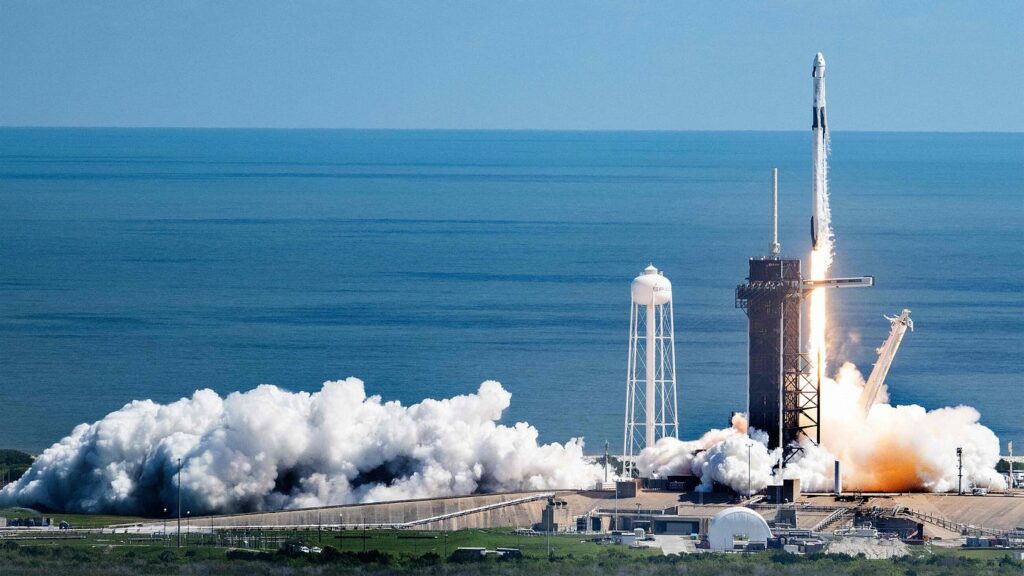

Privately owned businesses are assuming an undeniably significant part in space investigation, driving advancement and diminishing the expense of admittance to space.
Striking Turns of events:
SpaceX keeps on driving the confidential area in space investigation, with its reusable Hawk rockets definitely decreasing the expense of sending off payloads into space. The company’s Starship vehicle, which is still in the development stage, aims to transport crew members as well as cargo on missions to Mars, the Moon, and other planets.
Blue Origin, which Jeff Bezos started, is also making big progress. The company’s New Shepard spacecraft has been used for suborbital space tourism, and its larger New Glenn rocket, which was made for orbital missions, will compete with SpaceX’s Falcon rockets.
Rocket Lab and Virgin Galactic, for example, are concentrating on space tourism and small satellite launches, respectively. The space industry is becoming more diverse as a result of these initiatives, and new markets for commercial space activities are emerging.
Effects on the Space Sector:
The contribution of privately owned businesses is speeding up the speed of room investigation and making space more available. For the future of space exploration, their innovations in launch technology, spacecraft design, and space infrastructure are crucial.
However, the commercialization of space also raises concerns regarding regulation, the management of space debris, and the possibility of rivalries over resources in space.
Arising Patterns in Space Investigation
1. Space travel:

Space tourism is becoming a real thing, and a number of companies are now offering private citizens suborbital and orbital flights.
Recent Achievements:
Both the New Shepard of Blue Origin and the SpaceShipTwo of Virgin Galactic have successfully completed suborbital flights with paying customers. These missions offer a concise encounter of weightlessness and a perspective on Earth from the edge of room.
SpaceX has announced plans to carry a civilian crew around the Earth on its first entirely private mission to orbit. This mission could pave the way for future commercial spaceflights and represents a significant step forward in the growth of space tourism.
Opportunities and Challenges:
While space the travel industry presents energizing open doors for the business, it additionally faces critical difficulties, including significant expenses, security concerns, and the natural effect of incessant send-offs.
Prices are likely to fall as the industry develops, making space tourism more accessible to a wider range of people. The public’s interest in space and the future of space exploration could be profoundly affected by this.
2. Space Utilization of Resources:
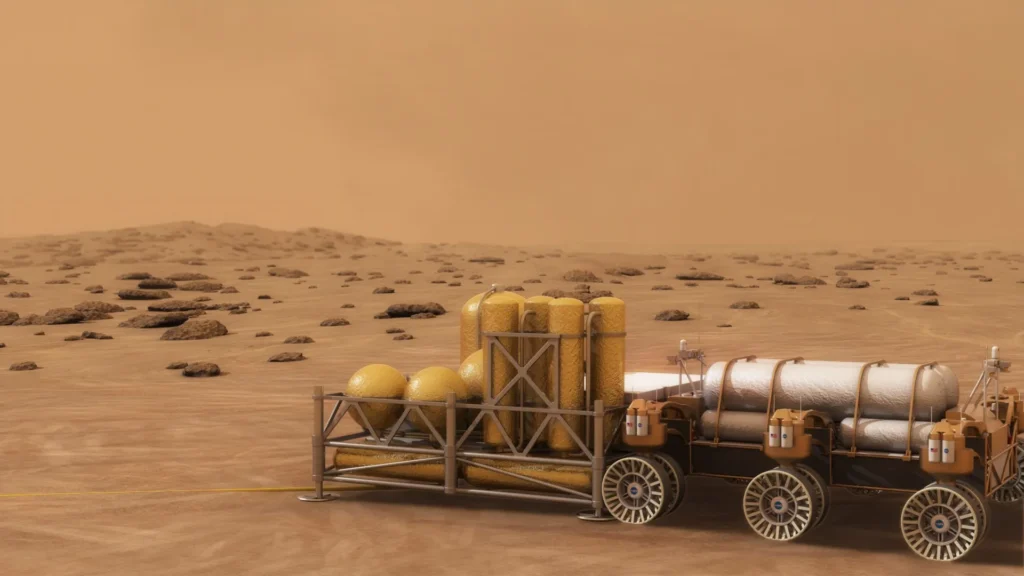

As space agencies and private businesses investigate the possibility of space-based economies, the idea of mining resources from the Moon, asteroids, and other celestial bodies is gaining traction.
Important Changes:
NASA’s Artemis program incorporates plans to investigate the extraction of lunar assets, for example, water ice, which could be utilized to deliver fuel and backing long haul lunar home. It is believed that these efforts are an important step toward sustainable space exploration.
Privately owned businesses, like Planetary Assets and Profound Space Enterprises, have been investigating the attainability of space rock mining. The objective of these endeavors is to extract valuable materials like platinum and rare earth elements that could either be utilized in space manufacturing or brought back to Earth.
Legal and Economic Implications:
The expansion of the use of space resources may result in the development of new business sectors and economic opportunities, potentially transforming the global economy.
However, the legal framework for the extraction of space resources is still developing. To meet the challenges and opportunities posed by space mining, international agreements like the Outer Space Treaty need to be updated.
3. Space Settlements and Habitats:
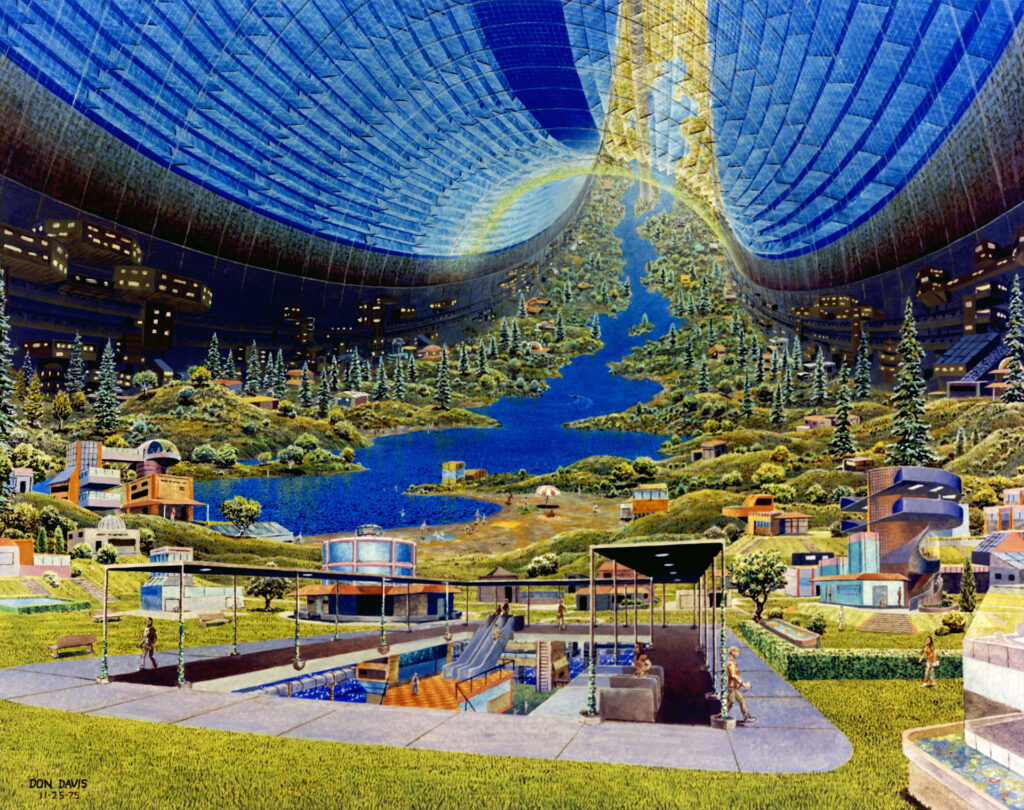

preparing for Life Beyond Earth As space exploration progresses, the possibility of establishing permanent human settlements on the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies grows.
Current Tasks:
NASA and its international partners are looking into the possibility of creating lunar habitats that could accommodate human missions for an extended period of time. These habitats would be constructed to shield astronauts from the harsh space environment, which includes high temperatures and radiation.
Companies like SpaceX are working on the technologies needed to transport and sustain human populations on Mars, so the idea of colonizing the Red Planet is also being considered. This includes the creation of life support systems, habitat modules, and methods for producing food that are sustainable.
Prospects and Challenges:
Laying out human environments in space presents various difficulties, including the requirement for dependable life emotionally supportive networks, security from space radiation, and the mental impacts of long haul seclusion.
In Conclusion,
Regardless of these difficulties, the possibility of room colonization is driving huge innovative work endeavors. A new chapter in human history could open if these projects succeed and human settlements are established on other planets.
The combination of government initiatives, international collaboration, and private sector innovation is driving the rapid advancement of space missions. Humanity is on the verge of becoming a multi-planet species as we push the boundaries of exploration. The changes discussed in this update are only a taste of the exciting times to come. Stay tuned for more information about the most recent space missions and the development of humanity’s ascent into space.



